Einstein's Physics: Atoms, Quanta, and Relativity - ...
https://books.google.com/books?isbn=0199669910
Ta-Pei Cheng - 2013 - Science
If the available thermal energy is not much bigger than this energy gap kBT ≲ △ε, ... On the other hand, Bose–Einstein condensation (BEC) is the phenomenon ..
kT is the product of the Boltzmann constant, k, and the temperature, T. This product is used in physics as a scaling factor for energy values in molecular-scale systems (sometimes it is used as a unit of energy), as the rates and frequencies of many processes and phenomena depend not on their energy alone, but on the ratio of that energy andkT, that is, on E / kT (see Arrhenius equation, Boltzmann factor). For a system in equilibrium in canonical ensemble, the probability of the system being in state with energy E is proportional to e−ΔE / kT. More fundamentally, kT is the amount of heat required to increase the thermodynamic entropy of a system, in natural units, by one nat.
In macroscopic scale systems, with large numbers of molecules, RT value is commonly used; its SI units are joules per mole (J/mol): (RT = kT ⋅ NA).
In statistical mechanics and mathematics, a Boltzmann distribution (also called Gibbs distribution[1]) is a probability distribution, probability measure, or frequency distribution of particles in a system over various possible states. The distribution is expressed in the form
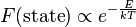
where  is state energy (which varies from state to state), and
is state energy (which varies from state to state), and 
 is state energy (which varies from state to state), and
is state energy (which varies from state to state), and 
No comments:
Post a Comment