Exact solutions in general relativity
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| This article may be confusing or unclear to readers. (March 2007) |
| General relativity |
|---|
  |
 .[1] (To wit, whenever a field is described by a Lagrangian, varying with respect to the field should give the field equations and varying with respect to the metric should give the stress-energy contribution due to the field.)
.[1] (To wit, whenever a field is described by a Lagrangian, varying with respect to the field should give the field equations and varying with respect to the metric should give the stress-energy contribution due to the field.)Finally, when all the contributions to the stress–energy tensor are added up, the result must satisfy the Einstein field equations (written here in geometrized units, where speed of light c = Gravitational constant G = 1)
 is the Einstein tensor, computed uniquely from the metric tensor which is part of the definition of a Lorentzian manifold. Since giving the Einstein tensor does not fully determine the Riemann tensor, but leaves the Weyl tensor unspecified (see the Ricci decomposition), the Einstein equation may be considered a kind of compatibility condition: the spacetime geometry must be consistent with the amount and motion of any matter or nongravitational fields, in the sense that the immediate presence "here and now" of nongravitational energy–momentum causes a proportional amount of Ricci curvature "here and now". Moreover, taking covariant derivatives of the field equations and applying the Bianchi identities, it is found that a suitably varying amount/motion of nongravitational energy–momentum can cause ripples in curvature to propagate as gravitational radiation, even across vacuum regions, which contain no matter or nongravitational fields.
is the Einstein tensor, computed uniquely from the metric tensor which is part of the definition of a Lorentzian manifold. Since giving the Einstein tensor does not fully determine the Riemann tensor, but leaves the Weyl tensor unspecified (see the Ricci decomposition), the Einstein equation may be considered a kind of compatibility condition: the spacetime geometry must be consistent with the amount and motion of any matter or nongravitational fields, in the sense that the immediate presence "here and now" of nongravitational energy–momentum causes a proportional amount of Ricci curvature "here and now". Moreover, taking covariant derivatives of the field equations and applying the Bianchi identities, it is found that a suitably varying amount/motion of nongravitational energy–momentum can cause ripples in curvature to propagate as gravitational radiation, even across vacuum regions, which contain no matter or nongravitational fields.Contents
[hide]Difficulties with the definition[edit]
Take any Lorentzian manifold, compute its Einstein tensor , which is a purely mathematical operation, divide by
, which is a purely mathematical operation, divide by  , and declare the resulting symmetric second rank tensor field to be the stress–energy tensor
, and declare the resulting symmetric second rank tensor field to be the stress–energy tensor  . Thus any Lorentzian manifold is a solution of the Einstein field equation with some right hand side. Which of course doesn't make general relativity useless, but only shows that there are two complementary ways to use it. One can fix the form of the stress–energy tensor (from some physical reasons, say) and study the solutions of the Einstein equations with such right hand side (for example, if the stress–energy tensor is chosen to be that of the perfect fluid, a spherically symmetric solution can serve as a stellar model). Alternatively, one can fix some geometrical properties of a spacetime and look for a matter source that could provide these properties. This is what cosmologists have done for the last 5–10 years: they assume that the Universe is homogeneous, isotropic, and accelerating and try to realize what matter (called dark energy) can support such a structure.
. Thus any Lorentzian manifold is a solution of the Einstein field equation with some right hand side. Which of course doesn't make general relativity useless, but only shows that there are two complementary ways to use it. One can fix the form of the stress–energy tensor (from some physical reasons, say) and study the solutions of the Einstein equations with such right hand side (for example, if the stress–energy tensor is chosen to be that of the perfect fluid, a spherically symmetric solution can serve as a stellar model). Alternatively, one can fix some geometrical properties of a spacetime and look for a matter source that could provide these properties. This is what cosmologists have done for the last 5–10 years: they assume that the Universe is homogeneous, isotropic, and accelerating and try to realize what matter (called dark energy) can support such a structure.Within the first approach the alleged stress–energy tensor must arise in the standard way from a "reasonable" matter distribution or nongravitational field. In practice, this notion is pretty clear, especially if you restrict the admissible nongravitational fields to the only one known in 1916, the electromagnetic field. But ideally we would like to have some mathematical characterization that states some purely mathematical test which we can apply to any putative "stress–energy tensor", which passes everything which might arise from a "reasonable" physical scenario, and rejects everything else. Unfortunately, no such characterization is known. Instead, we have crude tests known as the energy conditions, which are similar to placing restrictions on the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a linear operator. But these conditions, it seems, can satisfy no-one. On the one hand, they are far too permissive: they would admit "solutions" which almost no-one believes are physically reasonable. On the other, they may be far too restrictive: the most popular energy conditions are apparently violated by the Casimir effect.
Einstein also recognized another element of the definition of an exact solution: it should be a Lorentzian manifold (meeting additional criteria), i.e. a smooth manifold. But in working with general relativity, it turns out to be very useful to admit solutions which are not everywhere smooth; examples include many solutions created by matching a perfect fluid interior solution to a vacuum exterior solution, and impulsive plane waves. Once again, the creative tension between elegance and convenience, respectively, has proven difficult to resolve satisfactorily.
In addition to such local objections, we have the far more challenging problem that there are very many exact solutions which are locally unobjectionable, but globally exhibit causally suspect features such as closed timelike curves or structures with points of separation ("trouser worlds"). Some of the best known exact solutions, in fact, have globally a strange character.
Types of exact solution[edit]
Many well-known exact solutions belong to one of several types, depending upon the intended physical interpretation of the stress–energy tensor:- Vacuum solutions:
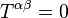 ; these describe regions in which no matter or nongravitational fields are present,
; these describe regions in which no matter or nongravitational fields are present,
- Electrovacuum solutions:
 must arise entirely from an electromagnetic field which solves the source-free Maxwell equations on the given curved Lorentzian manifold; this means that the only source for the gravitational field is the field energy (and momentum) of the electromagnetic field,
must arise entirely from an electromagnetic field which solves the source-free Maxwell equations on the given curved Lorentzian manifold; this means that the only source for the gravitational field is the field energy (and momentum) of the electromagnetic field,
- Null dust solutions:
 must correspond to a stress–energy tensor which can be interpreted as arising from incoherent electromagnetic radiation, without necessarily solving the Maxwell field equations on the given Lorentzian manifold,
must correspond to a stress–energy tensor which can be interpreted as arising from incoherent electromagnetic radiation, without necessarily solving the Maxwell field equations on the given Lorentzian manifold,
- Fluid solutions:
 must arise entirely from the stress–energy tensor of a fluid (often taken to be a perfect fluid); the only source for the gravitational field is the energy, momentum, and stress (pressure and shear stress) of the matter comprising the fluid.
must arise entirely from the stress–energy tensor of a fluid (often taken to be a perfect fluid); the only source for the gravitational field is the energy, momentum, and stress (pressure and shear stress) of the matter comprising the fluid.
- Scalar field solutions:
 must arise entirely from a scalar field (often a massless scalar field); these can arise in classical field theory treatments of meson beams, or as quintessence,
must arise entirely from a scalar field (often a massless scalar field); these can arise in classical field theory treatments of meson beams, or as quintessence,
- Lambdavacuum solutions (not a standard term, but a standard concept for which no name yet exists):
 arises entirely from a nonzero cosmological constant.
arises entirely from a nonzero cosmological constant.
Below we have sketched a classification by physical interpretation. This is probably more useful for most readers than the Segre classification of the possible algebraic symmetries of the Ricci tensor, but for completeness we note the following facts:
- nonnull electrovacuums have Segre type
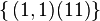 and isotropy group SO(1,1) x SO(2),
and isotropy group SO(1,1) x SO(2), - null electrovacuums and null dusts have Segre type
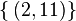 and isotropy group E(2),
and isotropy group E(2), - perfect fluids have Segre type
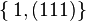 and isotropy group SO(3),
and isotropy group SO(3), - Lambdavacuums have Segre type
 and isotropy group SO(1,3).
and isotropy group SO(1,3).
Constructing solutions[edit]
The Einstein field equation, when fully written out as a system of partial differential equations, takes the form of a rather complicated system of coupled, nonlinear partial differential equations. As such, in general, it is very hard to solve.Nonetheless, several effective techniques for obtaining exact solutions are available.
The simplest involves imposing symmetry conditions on the metric tensor, such as stationarity (symmetry under time translation) or axisymmetry (symmetry under rotation about some symmetry axis). With sufficiently clever assumptions of this sort, it is often possible to reduce the Einstein field equation to a much simpler system of equations, even a single partial differential equation (as happens in the case of stationary axisymmetric vacuum solutions, which are characterized by the Ernst equation) or a system of ordinary differential equations (as happens in the case of the Schwarzschild vacuum).
This naive approach usually works best if one uses a frame field rather than a coordinate basis.
A related idea involves imposing algebraic symmetry conditions on the Weyl tensor, Ricci tensor, or Riemann tensor. These are often stated in terms of the Petrov classification of the possible symmetries of the Weyl tensor, or the Segre classification of the possible symmetries of the Ricci tensor. As will be apparent from the discussion above, such Ansätze often do have some physical content, although this might not be apparent from their mathematical form.
This second kind of symmetry approach has often been used with the Newman–Penrose formalism, which uses spinorial quantities for more efficient bookkeeping.
Even after such symmetry reductions, the reduced system of equations is often difficult to solve. For example, the Ernst equation is a nonlinear partial differential equation somewhat resembling the nonlinear Schrödinger equation (NLS).
But recall that the conformal group on Minkowski spacetime is the symmetry group of the Maxwell equations. Recall too that solutions of the heat equation can be found by assuming a scaling Ansatz. These notions are merely special cases of Sophus Lie's notion of the point symmetry of a differential equation (or system of equations), and as Lie showed, this can provide an avenue of attack upon any differential equation which has a nontrivial symmetry group. Indeed, both the Ernst equation and the NLS have nontrivial symmetry groups, and some solutions can be found by taking advantage of their symmetries. These symmetry groups are often infinite dimensional, but this is not always a useful feature.
Emmy Noether showed that a slight but profound generalization of Lie's notion of symmetry can result in an even more powerful method of attack. This turns out to be closely related to the discovery that some equations, which are said to be completely integrable, enjoy an infinite sequence of conservation laws. Quite remarkably, both the Ernst equation (which arises several ways in the studies of exact solutions) and the NLS turn out to be completely integrable. They are therefore susceptible to solution by techniques resembling the inverse scattering transform which was originally developed to solve the Korteweg-de Vries (KdV) equation, a nonlinear partial differential equation which arises in the theory of solitons, and which is also completely integrable. Unfortunately, the solutions obtained by these methods are often not as nice as one would like. For example, in a manner analogous to the way that one obtains a multiple soliton solution of the KdV from the single soliton solution (which can be found from Lie's notion of point symmetry), one can obtain a multiple Kerr object solution, but unfortunately, this has some features which make it physically implausible.[2]
There are also various transformations (see Belinski-Zakharov transform) which can transform (for example) a vacuum solution found by other means into a new vacuum solution, or into an electrovacuum solution, or a fluid solution. These are analogous to the Bäcklund transformations known from the theory of certain partial differential equations, including some famous examples of soliton equations. This is no coincidence, since this phenomenon is also related to the notions of Noether and Lie regarding symmetry. Unfortunately, even when applied to a "well understood", globally admissible solution, these transformations often yield a solution which is poorly understood and their general interpretation is still unknown.
Existence of solutions[edit]
Given the difficulty of constructing explicit small families of solutions, much less presenting something like a "general" solution to the Einstein field equation, or even a "general" solution to the vacuum field equation, a very reasonable approach is to try to find qualitative properties which hold for all solutions, or at least for all vacuum solutions. One of the most basic questions one can ask is: do solutions exist, and if so, how many?To get started, we should adopt a suitable initial value formulation of the field equation, which gives two new systems of equations, one giving a constraint on the initial data, and the other giving a procedure for evolving this initial data into a solution. Then, one can prove that solutions exist at least locally, using ideas not terribly dissimilar from those encountered in studying other differential equations.
To get some idea of "how many" solutions we might optimistically expect, we can appeal to Einstein's constraint counting method. A typical conclusion from this style of argument is that a generic vacuum solution to the Einstein field equation can be specified by giving four arbitrary functions of three variables and six arbitrary functions of two variables. These functions specify initial data, from which a unique vacuum solution can be evolved. (In contrast, the Ernst vacuums, the family of all stationary axisymmetric vacuum solutions, are specified by giving just two functions of two variables, which are not even arbitrary, but must satisfy a system of two coupled nonlinear partial differential equations. This may give some idea of how just tiny a typical "large" family of exact solutions really is, in the grand scheme of things.)
However, this crude analysis falls far short of the much more difficult question of global existence of solutions. The global existence results which are known so far turn out to involve another idea.
Global stability theorems[edit]
We can imagine "disturbing" the gravitational field outside some isolated massive object by "sending in some radiation from infinity". We can ask: what happens as the incoming radiation interacts with the ambient field? In the approach of classical perturbation theory, we can start with Minkowksi vacuum (or another very simple solution, such as the de Sitter lambdavacuum), introduce very small metric perturbations, and retain only terms up to some order in a suitable perturbation expansion—somewhat like evaluating a kind of Taylor series for the geometry of our spacetime. This approach is essentially the idea behind the post-Newtonian approximations used in constructing models of a gravitating system such as a binary pulsar. However, perturbation expansions are generally not reliable for questions of long-term existence and stability, in the case of nonlinear equations.The full field equation is highly nonlinear, so we really want to prove that the Minkowski vacuum is stable under small perturbations which are treated using the fully nonlinear field equation. This requires the introduction of many new ideas. The desired result, sometimes expressed by the slogan that the Minkowski vacuum is nonlinearly stable, was finally proven by Demetrios Christodoulou and Sergiu Klainerman only in 1993. Analogous results are known for lambdavac perturbations of the de Sitter lambdavacuum (Helmut Friedrich) and for electrovacuum perturbations of the Minkowski vacuum (Nina Zipser).
The positive energy theorem[edit]
Main article: Positive energy theorem
Another issue we might worry about is whether the net mass-energy of an isolated concentration of positive mass-energy density (and momentum) always yields a well-defined (and non-negative) net mass. This result, known as the positive energy theorem was finally proven by Richard Schoen and Shing-Tung Yau in 1979, who made an additional technical assumption about the nature of the stress–energy tensor. The original proof is very difficult; Edward Witten soon presented a much shorter "physicist's proof", which has been justified by mathematicians—using further very difficult arguments. Roger Penrose and others have also offered alternative arguments for variants of the original positive energy theorem.Examples[edit]
Noteworthy examples of vacuum solutions, electrovacuum solutions, and so forth, are listed in specialized articles (see below). These solutions contain at most one contribution to the energy–momentum tensor, due to a specific kind of matter or field. However, there are some notable exact solutions which contain two or three contributions, including:- NUT-Kerr–Newman–de Sitter solution contains contributions from an electromagnetic field and a positive vacuum energy, as well as a kind of vacuum perturbation of the Kerr vacuum which is specified by the so-called NUT parameter,
- Gödel dust contains contributions from a pressureless perfect fluid (dust) and from a positive vacuum energy.
- certain wormhole metrics (which can serve as a speculative toy model of a stargate held open by a hypothetical kind of exotic matter, as in 2001: A Space Odyssey; also a toy model of hypothetical time machine, see below),
- Alcubierre metric (which has been used as a speculative toy model of effectively superluminal space travel, as in the warp drive from Star Trek).
- "Time machines", i.e. initially nice spacetimes in which at some stage of evolution closed causal curves appear.
Nature of spacetime 4-vector and tangent space?
An entry level confusion about spacetime. I understand that a 4-vector describes a point or event in spacetime. But I've also read (Bertschinger, 1999) that re spacetime "we are discussing tangent vectors that lie in the tangent space of the manifold at each point". If a point/event is described by a single 4-vector, what are all these tangent vectors that lie on the same point? Do they have different co-ordinates to the 'point/event' 4-vector? Could I also ask how a 4-vector 'contains' any sense of direction (I'm thinking here of a vector having direction and magnitude)?
| |||
Your confusion comes from the difference between special and general relativity. In special relativity, the space-time manifold is assumed to carry the structure of 4-dimensional Minkowski space, which has the nice property that it is canonically identified with its own tangent space at the origin (since it is a vector space). So in special relativity you can speak of a space-time event as a 4-vector, and you can also speak of global Lorentz transformations (by doing the local Lorentz transformation in the tangent space and propagating the transformation to the whole space-time using the canonical identification).
In general relativity, however, the space-time is allowed to be an arbitrary Lorentzian manifold (what we do is break the global Lorentz symmetry of Minkowski space and require it to only hold infinitesimally, i.e. on the tangent space), and you don't have a canonical way of identifying the entire space-time with the tangent space of a fixed point. Therefore you cannot speak of a space-time event (now just a point in your space-time manifold) as a 4-vector! Edit Let me try to make the difference between an affine and non-affine space more apparent. Let us start by considering a two dimensional manifold. In fact, we'll just compare the usual flat plane and the sphere. On the plane, we can fix an arbitrary point and call it the origin. Starting from this origin, pick a direction, and call it the
On the sphere, however, you can again fix an arbitrary point and call it the "origin", and a direction which we call "
Now, going back to the plane, if instead you start by going "face But on the sphere, if you start by "face What does this mean? On a flat plane, from the above demonstration, after fixing an origin and a direction On the surface of the sphere (a curved manifold), however, the above example shows that the intuition we learned from studying classical mechanics about using vector addition for the "displacement vector" cannot hold for the positions of points. So you shouldn't think about space-time events in general relativity (which is a point on some possibly curved manifold), as vectors relative to a fixed origin. (Because with vectors you would be tempted to add them and so forth.) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Think of a liquid that is flowing in two dimensions on a flat surface. At every point we can draw a vector that points in the direction that the fluid is flowing in at that point. That is a vector in the vector space at that point, the tangent space. There is a tangent space at every point, because at every point the fluid could be flowing in any direction, although an equation of motion might require, for example, continuity from point to point. An example of a vector flow (found through Google images for "fluid flow") is http://www.dstu.univ-montp2.fr/geofracnet/Images/connollyflownet2.jpg. Graphically, of course, the tangent vectors to the flow can only be displayed at a finite number of points, but from the point of view of a differential equation there's a flow vector at every point. All the tangent spaces are exactly the same as all the others.
The "vectors" used to describe the points are vectors in the vector space at one particular point, the center of the coordinate system, with the vector describing the location of the other point relative to the center of the coordinate system as distances in two directions that aren't parallel. The four-dimensional case is no different provided we concern ourselves only with vector spaces, but the idea of a Lorentzian distance is of course different from the idea of a Euclidean distance. In coordinate terms, we could talk of two functions, A vector in 2 or in 4 dimensions can of course represent something other than a velocity field. In due course you will get straight what can be represented by vectors and what requires tensors. Now imagine a fluid flowing on the surface of a sphere. Again there is a tangent space at every point on the surface of the sphere, and all the tangent spaces are exactly the same as the others, but now it's harder to describe explicitly the way in which the many tangent spaces are the same as each other. Saying which point is which by using vectors in a tangent space at a specific point is also more problematic. | |||||||||||||
|
