Magnetic ForceThe magnetic field B is defined from the Lorentz Force Law, and specifically from the magnetic force on a moving charge: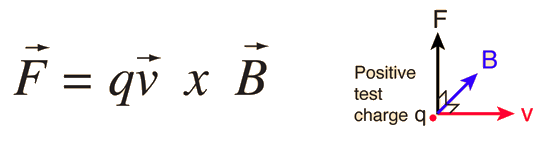 1. The force is perpendicular to both the velocity v of the charge q and the magnetic field B. 2. The magnitude of the force is F = qvB sinθ where θ is the angle < 180 degrees between the velocity and the magnetic field. This implies that the magnetic force on a stationary charge or a charge moving parallel to the magnetic field is zero. 3. The direction of the force is given by the right hand rule. The force relationship above is in the form of a vector product. 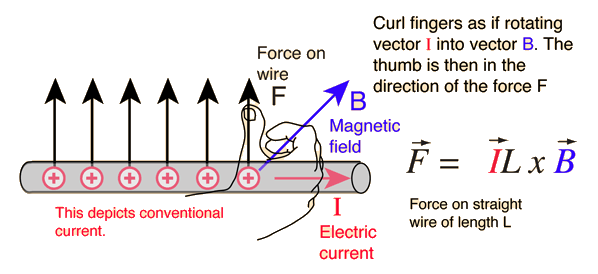 From the force relationship above it can be deduced that the units of magnetic field are Newton seconds /(Coulomb meter) or Newtons per Ampere meter. This unit is named the Tesla. It is a large unit, and the smaller unit Gauss is used for small fields like the Earth's magnetic field. A Tesla is 10,000 Gauss. The Earth's magnetic field at the surface is on the order of half a Gauss.
| Index Electromagnetic force Magnetic field concepts | ||
| Go Back |
Lorentz Force LawBoth the electric field and magnetic field can be defined from the Lorentz force law: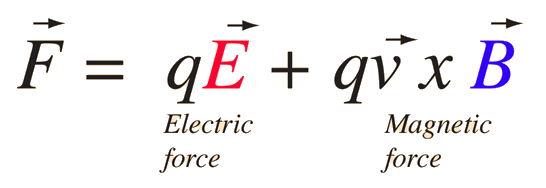 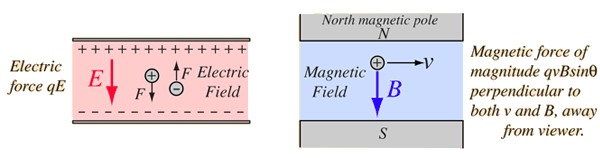 | Index Electromagnetic force Magnetic force Magnetic field concepts | ||
| Go Back |
Right Hand Rule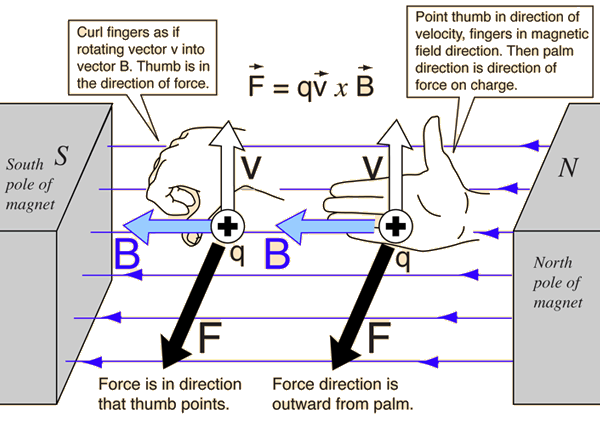 For applications to current-carrying wires, the conventional electric current direction can be substituted for the charge velocity v in the above digram. 
| Index Magnetic force Magnetic field concepts | ||
|
No comments:
Post a Comment